The COVID-19 outbreak has been out for more than a year. Except for the D614G variant, which was detected early, increased its transmission capacity and quickly occupied the world, the currently widely concerned SARS-CoV-2 variant is N501Y. After October 2020, SARS-CoV -2 N501Y mutations in RBD suddenly began to appear in large numbers. A number of studies have explained from multiple perspectives that N501Y can enhance its infectivity by enhancing its binding force to host ACE2, but there is no immune escape, regardless of natural infection in recovered patients. Serum, or healthy human serum vaccinated with Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, did not reduce the neutralizing titer of N501Y. Up to now, there are three main lineages containing N501Y: 1) 501Y.V1 (B.1.1.7, Alpha mutant) first discovered in the UK; 2) 501Y.V2 (B.1.351, first discovered in South Africa) Beta mutant strain); 3) 501Y.V3 (P.1, Gamma mutant strain) first discovered in Brazil.
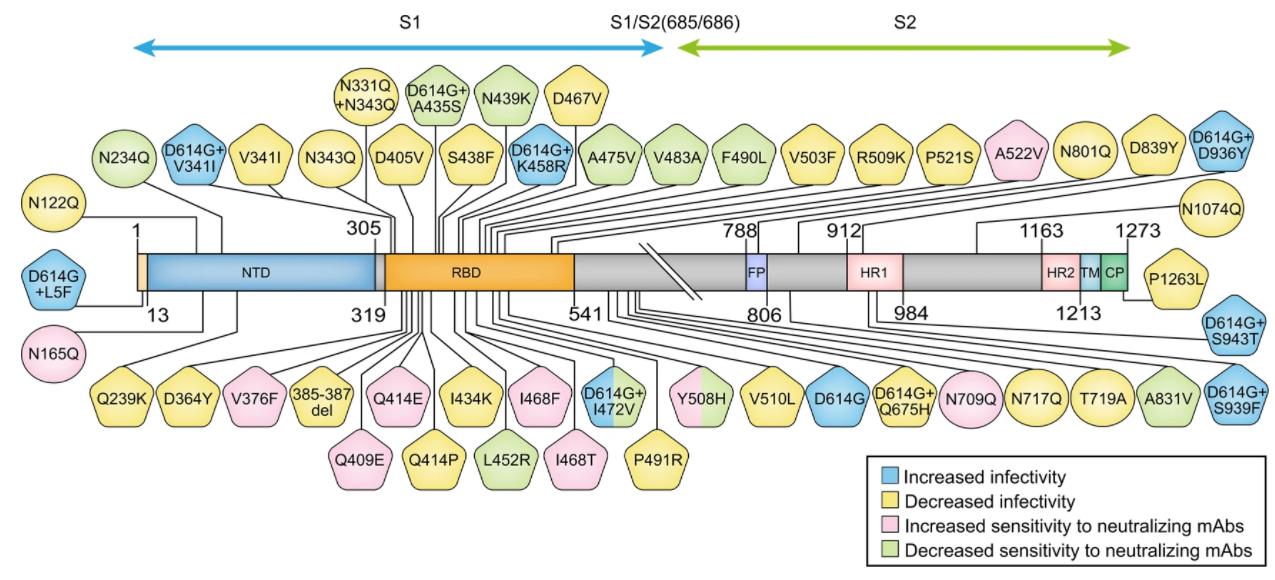
The S protein mutations of 501Y.V1 also include 69-70del, 144del, 570D, 681H, 716I, and 982A. This mutant strain is also known as Alpha mutant strain: B.1.1.7, first appeared in the UK, mutations on the spike protein were N501Y, D614G; the direct consequence was to change the virus’ infectivity and increase the transmission speed by 50%; The sensitivity to monoclonal antibody therapy remains unchanged; it can also be effectively neutralized by antibodies produced by vaccines or natural infections.
The S protein mutations of 501Y.V2 also include 80A, 215G, 242-243del, 417N, 484K, and 701N. This mutant strain is also called Beta mutant strain: B.1.351, first appeared in South Africa, the main mutations on the spike protein are K417N, E484K, N501Y; the direct consequence is a 50% increase in infectivity; against monoclonal antibodies The sensitivity of treatment is reduced; the neutralizing effect of antibodies produced by vaccines or natural infections is also significantly reduced.
The S protein mutations of 501Y.V3 also include 18F, 20N, 26S, 138Y, 190S, 417T, 484K, 655Y, 1027I. This variant is also known as the Gamma mutant: P.1, first appeared in Japan and Brazil, the main mutations on the spike protein are K417T, E484K, N501Y; the direct consequence is mainly sensitivity to monoclonal antibody therapy The neutralization effect of antibodies produced by vaccines or natural infections is also significantly reduced.
Many of the above mutation sites have appeared in chronic infections of immunodeficiency patients. The special environment in immunodeficiency patients and the pressure of plasma or antibody treatment will cause the accelerated evolution of SARS-CoV-2, and then a certain degree of immune escape, such as E484K has been reported in a number of studies to have strong immune escape ability. It has obvious resistance to monoclonal antibodies C121, C144, 2B04, 2H04, 1B07, REGN-10989/34, etc.. And the serum also showed a certain degree of resistance for polyclonal to some recovered patients.
At present, there is preliminary evidence in the laboratory that most of the serum samples of recovered patients who have been naturally infected with SARS-CoV-2 still have neutralizing activity against the 501Y.V1 pseudovirus, and the neutralization of a small number of samples has decreased by 5 to 10 times; however, Researchers tested the serum samples of 16 volunteers vaccinated with RNA vaccine BNT162b2 21 days after the second injection, and found that the neutralizing activity of the pseudovirus did not decrease, indicating that 501Y.Y1 is likely not to escape RNA vaccination induction Immunity.
For 501Y.V2, after the researchers tested the serum of 44 recovered patients, they found that more than 90% of the serum’s escape ability was reduced to varying degrees, 48% of the serum completely lost its neutralizing ability, and only 7% of the severely ill recovered Patient ID50 is greater than 400. The researchers further constructed the RBD three-mutated (K417N, E484K, N501Y) strain in 501Y.V2 and found that 27% of the serum lost its neutralizing activity, but there was still 23% of the serum ID50 (median infectious dose) is greater than 400, which also indicates that NTD mutations also contribute to escape; however, the researchers tested samples from 20 volunteers eight weeks after the second injection of mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 vaccine and found that The neutralizing ability of the three-mutation (K417N, E484K, N501Y) pseudovirus is only reduced by 1 to 3 times. Of the monoclonal antibodies isolated from volunteers, only 26% of the antibody binding was reduced by at least 5 times, and 17 antibodies with strong neutralizing activity were neutralized, and 9 of them were found to have at least a 10 reduction in the neutralizing activity of E484K. 5 of them were found to have at least a 10 times in the neutralizing activity of K417N, and 4 is reduced by at least 10 times for N501Y. These studies show that 501Y.V2 has a certain degree of escape ability.
At present, there are few studies on the escape of the 501Y.V3 strain. In general, the polyclonal serum induced by the mRNA vaccine has a much stronger ability to resist mutations of the strain than the serum transformed by natural infection.
In addition to the above-mentioned mutant strains, 3 more mutant strains were listed as “Variants of Concern” by the CDC in the United States:
Epsilon mutant strain: B.1.427, first appeared in California, USA. The main mutation on the spike protein is L452R; the direct result is an increase in infectivity by 20%; antibodies produced by vaccines or natural infections have a significantly reduced neutralization effect; There is a slight decrease in sensitivity to monoclonal antibody therapy.
Epsilon mutant strain: B.1.429, first appeared in California, USA, the main mutation on the spike protein is L452R; the direct result is an increase in infectivity by 20%; the neutralizing effect of antibodies produced by vaccines or natural infections is significantly reduced; There is a slight decrease in sensitivity to monoclonal antibody therapy.
Delta mutant strain: B.1.617.2, first appeared in India, the main mutation on the spike protein is L452R; increased infectivity.
