Clinically, some people often have repeated allergies, eczema and respiratory infections or other parts of the infection, in this case, in addition to some routine tests such as tests for white blood cells, immunoglobulin series, lymphocyte subsets, etc., the five immune immunoglobulin tests are also necessary. Although many people do these tests in the doctor’s advice, they do not know its role or clinical significance. Here you can find an explanation.
1. What is immunoglobulin?
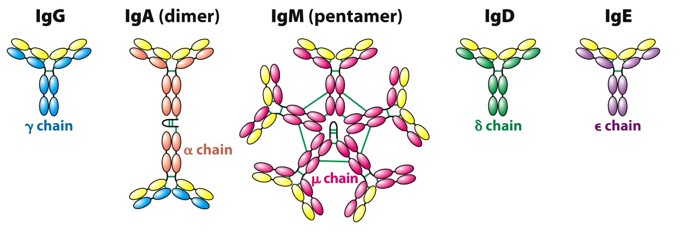
Immunoglobulin (Ig) refers to a class of globulin with antibody activity or with chemical structure similar to antibody, and it is the main reaction substances of humoral immune response. With anti-bacterial, anti-viral effect and strengthening the phagocytosis of cells function, as well as killing or dissolving pathogenic microorganisms in the complement of the collaboration, it is an important component of disease resistance in the body.
Immunoglobulin is produced by plasma cells, widely found in blood, tissue fluid and exocrine fluid, accounting for about 20% of the total plasma protein. At present there are five classes of Ig found in the human body, namely IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE, IgD.
Five Immunoglobulin tests include IgA (immunoglobulin A), IgG (immunoglobulin G), IgM (immunoglobulin M), complement C3 and C4.
Immunoglobulin is produced by plasma cells, widely found in blood, tissue fluid and exocrine fluid, accounting for about 20% of the total plasma protein. At present there are five classes of Ig found in the human body, namely IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE, IgD.
Five Immunoglobulin tests include IgA (immunoglobulin A), IgG (immunoglobulin G), IgM (immunoglobulin M), complement C3 and C4.
2. Clinical significance of five immunoglobulin tests
IgG
IgG is synthesized from plasma cells and is the only antibody that can pass through the placenta barrier. It can be synthesized 3 months after birth. IgG is the most abundant in normal human serum, accounting for 3/4 of total serum Ig, which is the most important anti-pathogenic microorganism antibody (re-immune response antibody) in body fluids and the main category of autoantibody in autoimmune disease.
Increased: chronic liver disease, subacute or chronic infection, connective tissue disease, IgG myeloma, or asymptomatic monoclonal IgG disease.
Decreased: hereditary or acquired antibody deficiency, mixed immunodeficiency syndrome, selective IgG deficiency, protein loss enteropathy, nephrotic syndrome, ankylosing muscular dystrophy, or immunosuppressive therapy.
IgA
IgA is mainly distributed in various mucosal surfaces and saliva, colostrum, tear, sweat, nasal secretions, bronchial secretions and digestive tract secretion, participating in the body’s mucosal local anti-infective immune response. IgA can not pass through the placental barrier, thus newborn babies can only get IgA from breast milk, but 4 to 6 months after birth they can start their own synthesis, and the synthesis level up to 25% of adults in 1-year-old, 8-year-old can reach adult level.
Increased: chronic liver disease, subacute or chronic infectious diseases (such as tuberculosis, fungal infections, etc.), autoimmune diseases (such as SLE, rheumatoid arthritis), cystic fibrosis, familial neutropenia, breast cancer, IgA nephropathy, IgA myeloma, and etc.
Decreased: hereditary or acquired antibody deficiency, immunodeficiency disease, selective IgA deficiency, no gamma-globulinemia, protein loss of bowel disease, burns and so on.
IgM
IgM, also known as macroglobulin, mainly distribute in the blood, accounting for 1/10 total amount of serum Ig. IgM is the earliest synthetic antibody in individual development. When the body is infected, IgM antibodies are the first to produce the primary immune response to the antibody.
Increased: fetal intrauterine infection, neonatal TORCH group, chronic or subacute infection, malaria, infectious mononucleosis, mycoplasma pneumonia, liver disease, connective tissue disease, macroglobulinemia, asymptomatic monoclonal IgM Sick and so on.
Decreased: hereditary or acquired antibody deficiency, mixed immunodeficiency syndrome, selective IgM deficiency, protein loss enteropathy, burns, anti-Ig antibody syndrome (mixed cryoglobulinemia), immunosuppressive agents Treatment and so on.
Complement C3 and C4
Blood complement content and activity in many pathological conditions will change.
Increased: acute rheumatoid disease, acute hepatitis, pneumonia, thyroiditis and other diseases;
Decreased: SLE patients, severe liver disease and malnutrition, other rheumatic diseases.
3. Under what circumstances need to do immunoglobulin five test?
— Children and adults with repeated sick;
— Autoimmune or atopic reactive disease;
— IgG4-related diseases;
— Immune deficiency disease;
— Other chronic diseases that occur immunoglobulin abnormalities: such as chronic kidney disease, neurological diseases, blood diseases, tumors, etc.
In short, if someone encountered these conditions, especially repeated infections, he need not forget to do an immunoglobulin test, so as not to miss the best treatment time.